Sec section analyzer development
Analyzers are shipped as Docker images to execute within a CI pipeline context. This guide describes development and testing practices across analyzers.
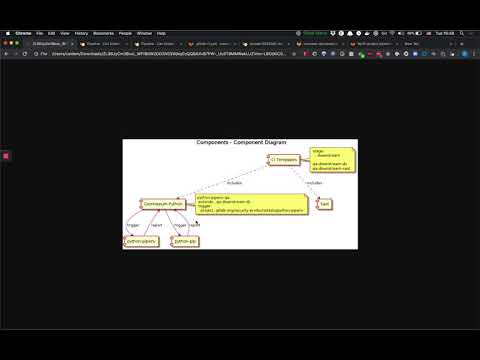
Shared modules
There are a number of shared Go modules shared across analyzers for common behavior and interfaces:
- The
commandGo package implements a CLI interface. - The
commonproject provides miscellaneous shared modules for logging, certificate handling, and directory search capabilities. - The
reportGo package’sReportandFindingstructs marshal JSON reports. - The
templateproject scaffolds new analyzers.
How to use the analyzers
Analyzers are shipped as Docker images. For example, to run the Semgrep Docker image to scan the working directory:
-
cdinto the directory of the source code you want to scan. - Run
docker login registry.gitlab.comand provide username plus personal or project access token with at least theread_registryscope. -
Run the Docker image:
docker run \ --interactive --tty --rm \ --volume "$PWD":/tmp/app \ --env CI_PROJECT_DIR=/tmp/app \ -w /tmp/app \ registry.gitlab.com/gitlab-org/security-products/analyzers/semgrep:latest /analyzer run - The Docker container generates a report in the mounted project directory with a report filename corresponding to the analyzer category. For example, SAST generates a file named
gl-sast-report.json.
Analyzers development
To update the analyzer:
- Modify the Go source code.
- Build a new Docker image.
- Run the analyzer against its test project.
- Compare the generated report with what’s expected.
Here’s how to create a Docker image named analyzer:
docker build -t analyzer .
For example, to test Secret Detection run the following:
wget https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/security-products/ci-templates/-/raw/master/scripts/compare_reports.sh
sh ./compare_reports.sh sd test/fixtures/gl-secret-detection-report.json test/expect/gl-secret-detection-report.json \
| patch -Np1 test/expect/gl-secret-detection-report.json && Git commit -m 'Update expectation' test/expect/gl-secret-detection-report.json
rm compare_reports.sh
You can also compile the binary for your own environment and run it locally
but analyze and run probably won’t work
since the runtime dependencies of the analyzer are missing.
Here’s an example based on SpotBugs:
go build -o analyzer
./analyzer search test/fixtures
./analyzer convert test/fixtures/app/spotbugsXml.Xml > ./gl-sast-report.json
Execution criteria
Enabling SAST requires including a pre-defined template to your GitLab CI/CD configuration.
The following independent criteria determine which analyzer needs to be run on a project:
- The SAST template uses
rules:existsto determine which analyzer will be run based on the presence of certain files. For example, the Brakeman analyzer runs when there are.rbfiles and aGemfile. - Each analyzer runs a customizable match interface before it performs the actual analysis. For example: Flawfinder checks for C/C++ files.
- For some analyzers that run on generic file extensions, there is a check based on a CI/CD variable. For example: Kubernetes manifests are written in YAML, so Kubesec runs only when
SCAN_KUBERNETES_MANIFESTSis set to true.
Step 1 helps prevent wastage of CI/CD minutes that would be spent running analyzers not suitable for the project. However, due to technical limitations, it cannot be used for large projects. Therefore, step 2 acts as final check to ensure a mismatched analyzer is able to exit early.
How to test the analyzers
Video walkthrough of how Dependency Scanning analyzers are using downstream pipeline feature to test analyzers using test projects:
Testing local changes
To test local changes in the shared modules (such as command or report) for an analyzer
you can use the
go mod replace
directive to load command with your local changes instead of using the version of command that has been
tagged remotely. For example:
go mod edit -replace gitlab.com/gitlab-org/security-products/analyzers/command/v3=/local/path/to/command
Alternatively you can achieve the same result by manually updating the go.mod file:
module gitlab.com/gitlab-org/security-products/analyzers/awesome-analyzer/v2
replace gitlab.com/gitlab-org/security-products/analyzers/command/v3 => /path/to/command
require (
...
gitlab.com/gitlab-org/security-products/analyzers/command/v3 v2.19.0
)
Testing local changes in Docker
To use Docker with replace in the go.mod file:
- Copy the contents of
commandinto the directory of the analyzer.cp -r /path/to/command path/to/analyzer/command. - Add a copy statement in the analyzer’s
Dockerfile:COPY command /command. - Update the
replacestatement to make sure it matches the destination of theCOPYstatement in the step above:replace gitlab.com/gitlab-org/security-products/analyzers/command/v3 => /command
Analyzer scripts
The analyzer-scripts repository contains scripts that can be used to interact with most analyzers. They enable you to build, run, and debug analyzers in a GitLab CI-like environment, and are particularly useful for locally validating changes to an analyzer.
For more information, refer to the project README.
Versioning and release process
Analyzers are independent projects that follow their own versioning. Patch version bumps tend to correspond to a Minor version bump of the underlying tools (i.e. bandit), allowing us greater flexibility in reserving Minor bumps for more significant changes to our scanners. In case of breaking changes imposed by the wrapped scanner, creating a new analyzer on a separate repository must be considered.
The analyzers are released as Docker images following this scheme:
- each push to the
masterbranch will override theedgeimage tag - each push to any
awesome-featurebranch will generate a matchingawesome-featureimage tag - each Git tag will generate the corresponding
Major.Minor.Patchimage tag. A manual job allows to override the correspondingMajorand thelatestimage tags to point to thisMajor.Minor.Patch.
To release a new analyzer Docker image, there are two different options:
- Manual release process
- Automatic release process
Manual release process
- Ensure that the
CHANGELOG.mdentry for the new analyzer is correct. - Ensure that the release source (typically the
masterormainbranch) has a passing pipeline. - Create a new release for the analyzer project by selecting the Deployments menu on the left-hand side of the project window, then selecting the Releases sub-menu.
- Select New release to open the New Release page.
- In the Tag name drop down, enter the same version used in the
CHANGELOG.md, for examplev2.4.2, and select the option to create the tag (Create tag v2.4.2here). - In the Release title text box enter the same version used above, for example
v2.4.2. - In the
Release notestext box, copy and paste the notes from the corresponding version in theCHANGELOG.md. - Leave all other settings as the default values.
- Select Create release.
- In the Tag name drop down, enter the same version used in the
After following the above process and creating a new release, a new Git tag is created with the Tag name provided above. This triggers a new pipeline with the given tag version and a new analyzer Docker image is built.
If the analyzer uses the analyzer.yml template, then the pipeline triggered as part of the New release process above automatically tags and deploys a new version of the analyzer Docker image.
If the analyzer does not use the analyzer.yml template, you’ll need to manually tag and deploy a new version of the analyzer Docker image:
- Select the CI/CD menu on the left-hand side of the project window, then select the Pipelines sub-menu.
- A new pipeline should currently be running with the same tag used previously, for example
v2.4.2. - After the pipeline has completed, it will be in a
blockedstate. - Select the
Manual jobplay button on the right hand side of the window and selecttag versionto tag and deploy a new version of the analyzer Docker image.
Use your best judgment to decide when to create a Git tag, which will then trigger the release job. If you can’t decide, then ask for other’s input.
Automatic release process
The following must be performed before the automatic release process can be used:
- Configure
CREATE_GIT_TAG: trueas aCI/CDenvironment variable. - Check the
Variablesin the CI/CD project settings. Unless the project already inherits theGITLAB_TOKENenvironment variable from the project group, create a project access token withcomplete read/write access to the APIand configureGITLAB_TOKENas aCI/CDenvironment variable which refers to this token.
After the above steps have been completed, the automatic release process executes as follows:
- A project maintainer merges an MR into the default branch.
- The default pipeline is triggered, and the
upsert git tagjob is executed.- If the most recent version in the
CHANGELOG.mdmatches one of the Git tags, the job is a no-op. - Else, this job automatically creates a new release and Git tag using the releases API. The version and message is obtained from the most recent entry in the
CHANGELOG.mdfile for the project.
- If the most recent version in the
- A pipeline is automatically triggered for the new Git tag. This pipeline releases the
latest,major,minorandpatchDocker images of the analyzer.
Steps to perform after releasing an analyzer
- After a new version of the analyzer Docker image has been tagged and deployed, please test it with the corresponding test project.
-
Announce the release on the relevant group Slack channel. Example message:
FYI I’ve just released
ANALYZER_NAMEANALYZER_VERSION.LINK_TO_RELEASE
Never delete a Git tag that has been pushed as there is a good chance that the tag will be used and/or cached by the Go package registry.