Protected tags all tiers
Protected tags:
- Allow control over who has permission to create tags.
- Prevent accidental update or deletion once created.
Each rule allows you to match either:
- An individual tag name.
- Wildcards to control multiple tags at once.
This feature evolved out of protected branches
Who can modify a protected tag
By default:
- To create tags, you must have the Maintainer role.
- No one can update or delete tags.
Configuring protected tags
To protect a tag, you must have at least the Maintainer role.
-
Go to the project’s Settings > Repository.
-
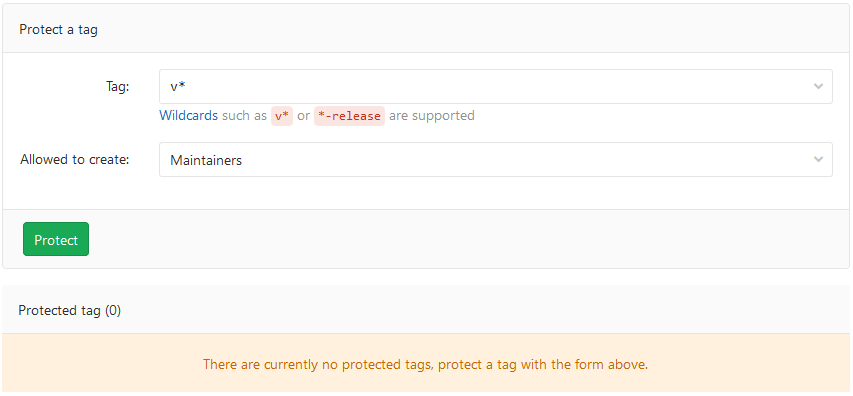
From the Tag dropdown list, select the tag you want to protect or type and select Create wildcard. In the screenshot below, we chose to protect all tags matching
v*: -
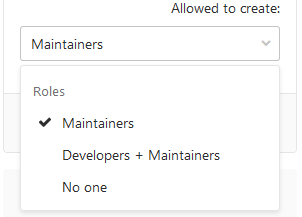
From the Allowed to create dropdown list, select users with permission to create matching tags, and select Protect:
-
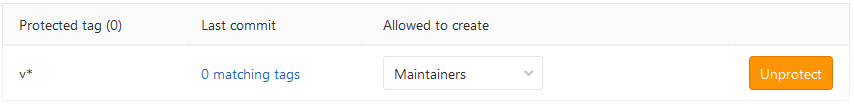
After done, the protected tag displays in the Protected tags list:
Wildcard protected tags
You can specify a wildcard protected tag, which protects all tags matching the wildcard. For example:
| Wildcard Protected Tag | Matching Tags |
|---|---|
v* |
v1.0.0, version-9.1
|
*-deploy |
march-deploy, 1.0-deploy
|
*gitlab* |
gitlab, gitlab/v1
|
* |
v1.0.1rc2, accidental-tag
|
Two different wildcards can potentially match the same tag. For example,
*-stable and production-* would both match a production-stable tag.
In that case, if any of these protected tags have a setting like
Allowed to create, then production-stable also inherit this setting.
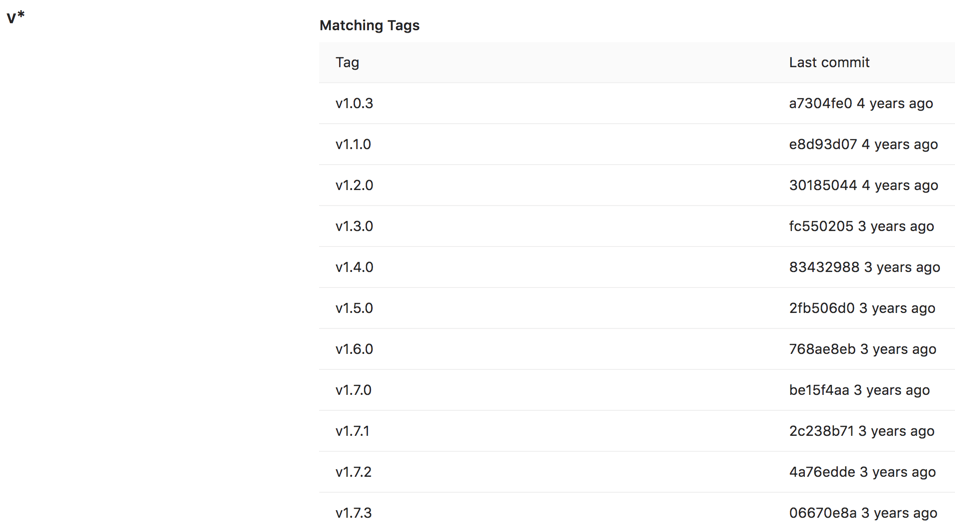
If you select a protected tag’s name, GitLab displays a list of all matching tags:
Prevent tag creation with the same name as branches
A tag and a branch with identical names can contain different commits. If your
tags and branches use the same names, users running git checkout
commands might check out the tag qa when they instead meant to check out
the branch qa.
To prevent this problem:
- Identify the branch names you do not want used as tags.
-
As described in Configuring protected tags, create a protected tag:
- For the Name, provide a name, such as
stable. You can also create a wildcard likestable-*to match multiple names, likestable-v1andstable-v2. - For Allowed to Create, select No one.
- Select Protect.
- For the Name, provide a name, such as
Users can still create branches, but not tags, with the protected names.
Allow deploy keys to create protected tags
Introduced in GitLab 15.11.
You can permit the owner of a deploy key to create protected tags. The deploy key works, even if the user isn’t a member of the related project. However, the owner of the deploy key must have at least read access to the project.
Prerequisites:
- The deploy key must be enabled for your project. A project deploy key is enabled by default when it is created. However, a public deploy key must be granted access to the project.
- The deploy key must have write access to your project repository.
To allow a deploy key to create a protected tag:
- On the top bar, select Main menu > Projects and find your project.
- On the left sidebar, select Settings > Repository.
- Expand Protected tags.
- From the Tag dropdown list, select the tag you want to protect.
- From the Allowed to create list, select the deploy key.
- Select Protect.
Delete a protected tag
You can manually delete protected tags with the GitLab API, or the GitLab user interface.
Prerequisite:
- You must have at least the Maintainer role in your project.
To do this:
- On the top bar, select Main menu > Projects and find your project.
- On the left sidebar, select Repository > Tags.
- Next to the tag you want to delete, select Delete ().
- On the confirmation dialog, enter the tag name and select Yes, delete protected tag.
Protected tags can only be deleted by using GitLab either from the UI or API. These protections prevent you from accidentally deleting a tag through local Git commands or third-party Git clients.